Table of Contents
- All About the Ebola Virus
- Ebola outbreak: 5 things you need to know now
- Ebola Virus Disease – Africa CDC
- ASLM Ebola Outbreak: Laboratory Workers as Key Partners
- Limited airborne transmission of Ebola is ‘very likely,’ new analysis ...
- Ebola (EBV): Overview and More
- 6 Things You Might Not Know About Ebola | Mental Floss
- Ebola: MedlinePlus
- What Happens After Surviving Ebola? | SiOWfa14 Science in Our World ...
- A History of Ebola in 24 Outbreaks - The New York Times
/EbolaVirus-5b7c3f08c9e77c0057d4924d.jpg)
/ebola_virus-56a09ae55f9b58eba4b20276.jpg)
What is Ebola?

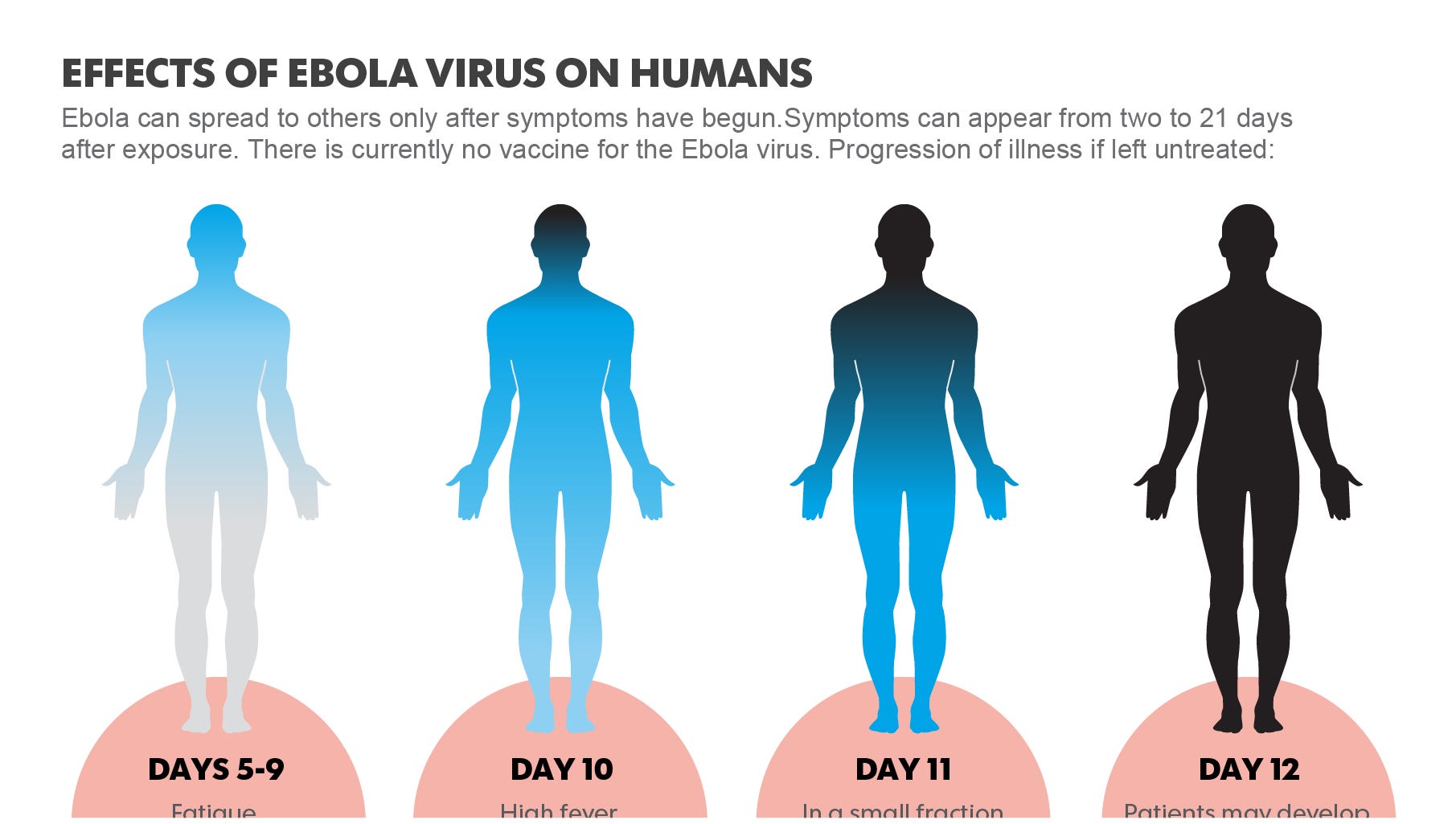
Symptoms of Ebola

How is Ebola Transmitted?
Ebola is transmitted through: Direct contact with infected blood, bodily fluids, or tissues Contact with objects contaminated with infected bodily fluids Close contact with an infected person, such as touching or caring for them Contact with infected animals, such as fruit bats or nonhuman primates The virus can also be spread through medical procedures, such as injections or surgeries, if proper infection control measures are not in place.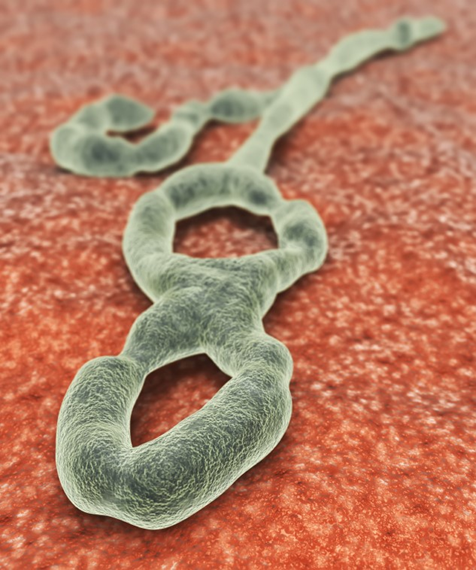
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling Ebola requires a multi-faceted approach. The CDC recommends: Avoiding close contact with people who are sick with Ebola Avoiding contact with infected bodily fluids Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and masks, when caring for patients Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing Avoiding eating or handling bushmeat, which can carry the virus The CDC also provides guidance on infection control and prevention in healthcare settings, including the use of PPE, proper disinfection and sterilization, and safe handling of medical waste.